Boilers (Steam and Hot Water)
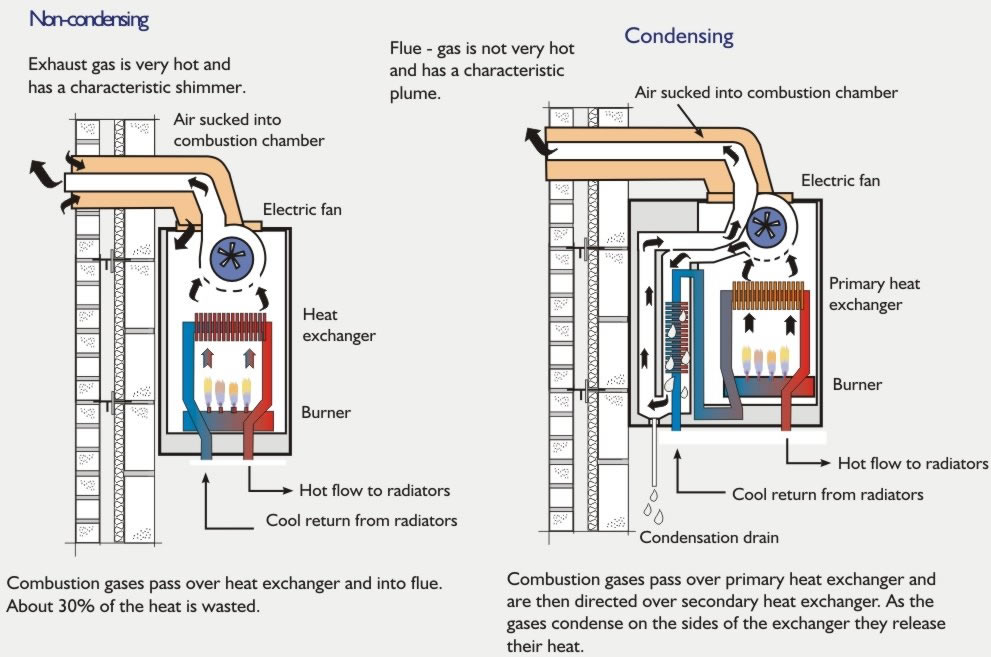
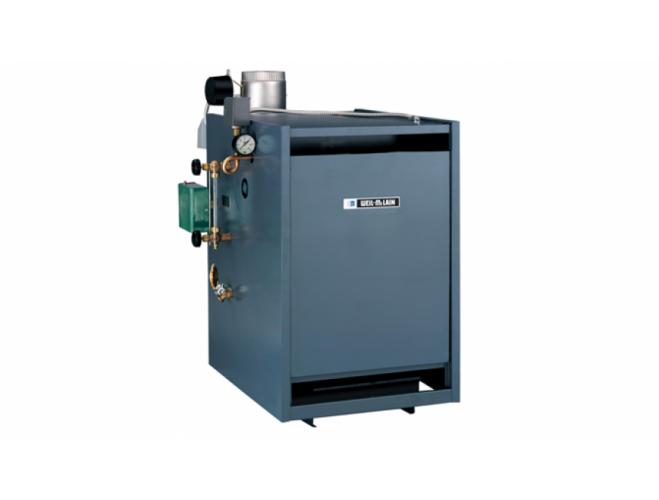
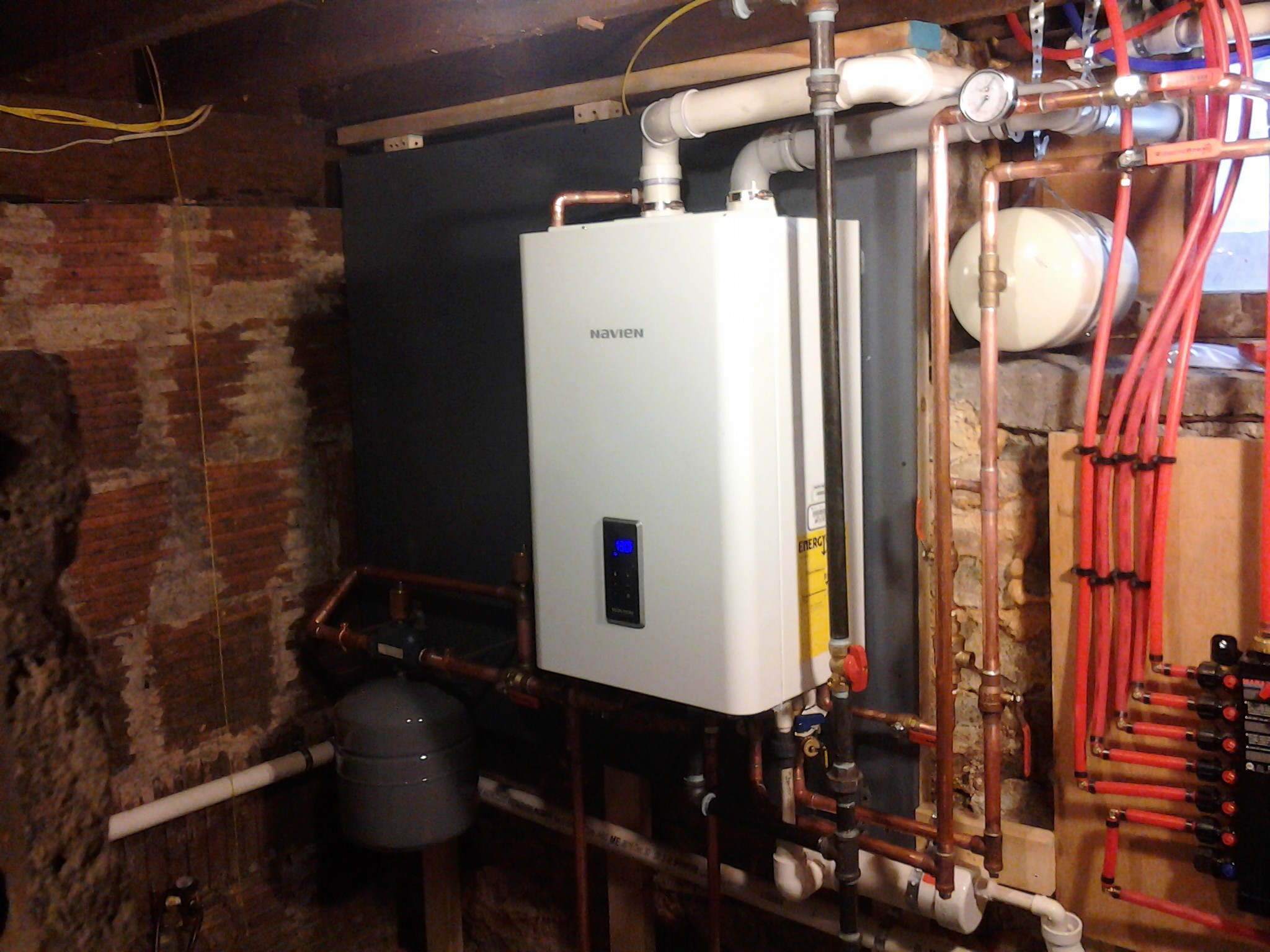
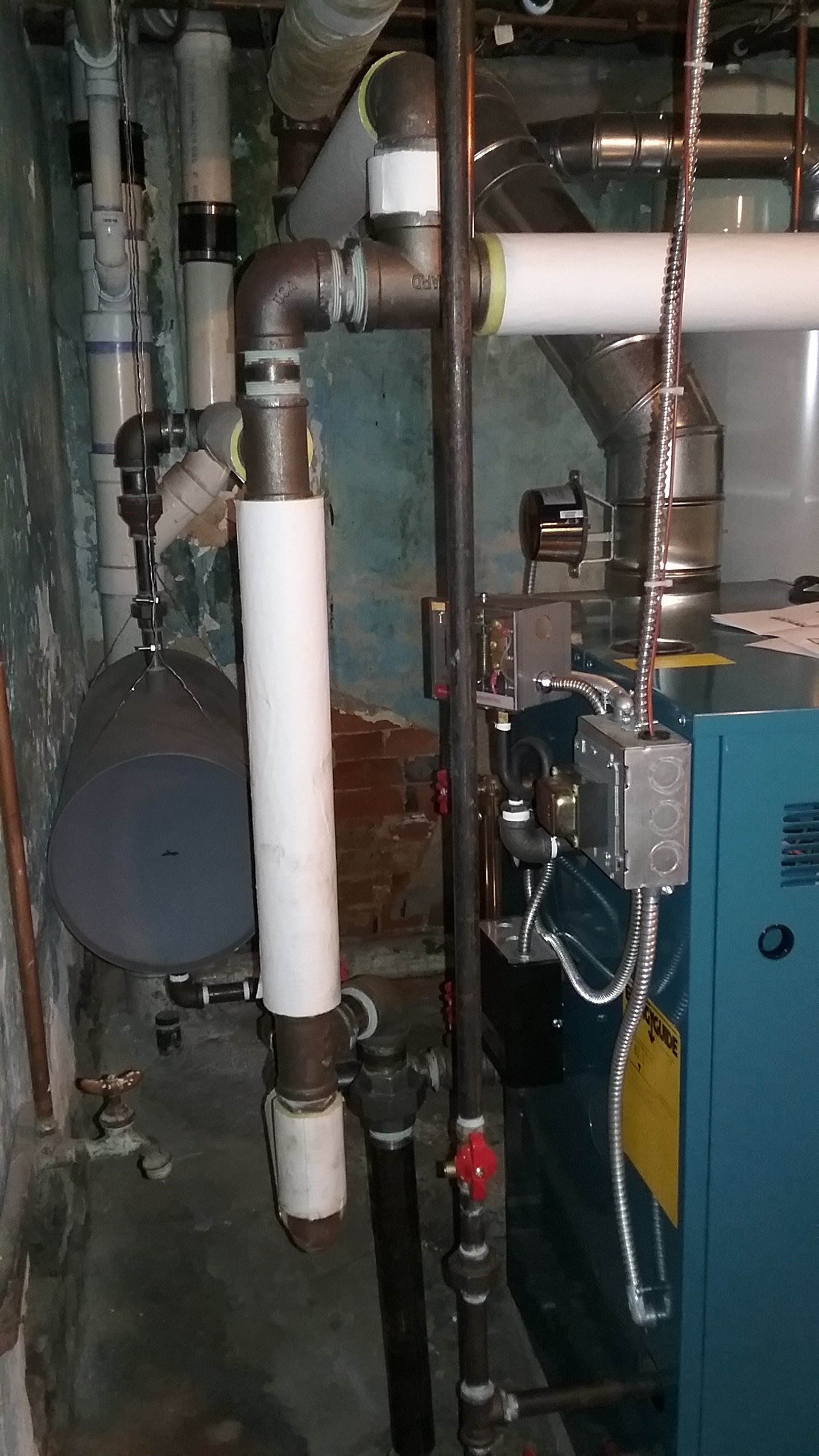
Boilers get there name from their history of creating steam for use in power production, central heating systems and use in locomotives. Boilers come in basically two types; hot water boilers and steam boilers. Steam Boilers heat the water in the boiler to a temperature that reaches the boiling point (212F depending on altitude). Steam takes up almost 1000 times more space (volume) as the same amount (volume) of water so the steam energy from expansion moves the steam through the piping to heat the different radiators of your home. There are older homes, businesses and churches as well as Penn State that use steam as a way of heating. Many of the older homes used hand fired coal boilers back in the day to heat the homes. This required a lot of manual labor to keep the houses warm by then. More current boiler technology uses water as a medium to transfer heat from the boiler to the home. Hot Water boilers do not boil the water but typically maintain water anywhere for 120F to 200F depending on the boiler and application. The boiler water temperature is regulated by an aquastat or similar control. The water is then pumped or circulated through piping to the various radiators, radiant tubing or baseboard radiation that then heats your room or house. Boilers efficiency is affected by the combustion efficiency of the fuel and the cleanliness of the heat exchanger. Soot is a byproduct of combustion that is seen if the fuel to air ratio is not properly set (normally more fuel than air). Oil and Wood boilers usually have the highest probability of creating soot. Gas or Propane boilers are typically the least likely of the boilers to create soot as they burn cleaner. It takes only 1/32 (less than a thickness of a dime) of a buildup of soot on the inside of a boiler heat exchanger to reduce the efficiency by 2%. The boiler efficiency drops off proportionally as the buildup continues. This is why it is good to have oil boilers serviced once a year. Most boilers have to run for 5 to 10 minutes until they come up to their efficiency ratings. Boilers that are too large can tend to short cycle and have the greatest probability of operating inefficiently. A properly sized and tuned boiler will give you the lowest operating cost and longest life. Boilers are rated in Btuh and by combustion efficiency. There is condensing and non-condensing technologies. Boilers that are 85% and lower are typically non-condensing. Boilers that are 85% to 95% efficiency are condensing boilers. Condensing boilers take advantage of the heat in the flue gases that normally are released up the chimney with less efficient boilers. Condensing Boilers have special heat exchangers in them that can handle the moisture that is precipitated out of the flue gases when heat is removed from it. This is called condensate and it is typically corrosive and will destroy a non-condensing boiler over time. Many of the condensing boilers have a small foot print with some that can be mounted on the wall giving more room in the home.
Give us a call to have us look over your application or replacement needs. We handle Steam, Condensing and Non-Condensing Boilers as well as almost any fuel. We install boilers throughout Centre County including , State College, Millheim, Bellefonte, Port Matilda including other nearby towns that are not in Centre County such as Lewistown, Lewisburg, Loch Haven and elsewhere.